Converting Performance Difference to Outcome Difference
| Input | Example: Comparison of AI-assisted diagnosis (intervention) and conventional diagnosis (control) | |
|---|---|---|
| ΔSensitivity | % | Sensitivity of AI-assisted diagnosis - Sensitivity of conventional diagnosis, for example, 5.0% |
| ΔSpecificity | % | Specificity of AI-assisted diagnosis - Specificity of conventional diagnosis, for example, -0.5% |
| Disease prevalence | % to % | For example, 5 to 8%. In case of a single value instead of a range, put in the same value for both boxes, for example, 5 to 5%. |
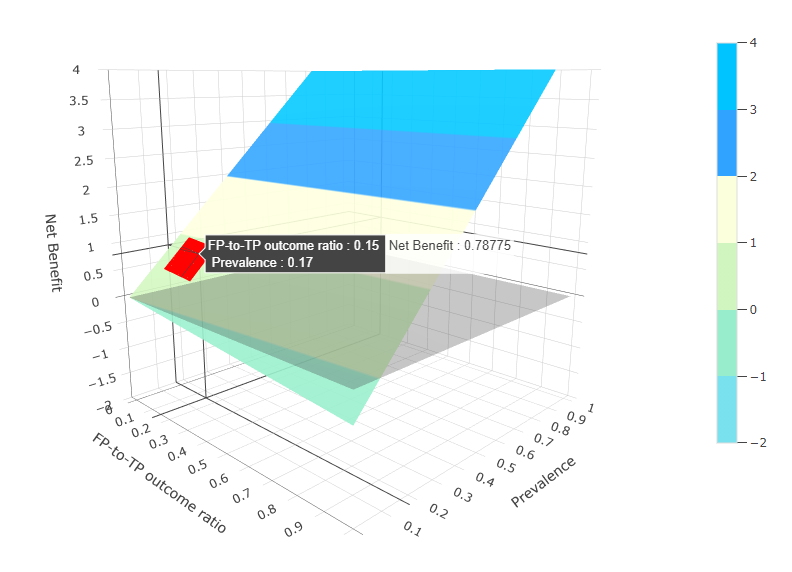
| FP-to-TP outcome ratio | to |
The ratio between the absolute amounts of net loss in patient outcome
incurred by an FP
decision
instead of leaving the
patient alone and net outcome gain provided by a TP decision compared
with neglecting the
disease in the patient, for
example, 0.05 to 0.1. In case of a single value instead of a range, put in the same value for both boxes, for example, 0.1 to 0.1. Taking surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma as an example, the ratio is A/B as shown below. A: Absolute amount of net outcome loss in a single FP patient = (negative consequences of unnecessary follow-up imaging tests, such as adverse effects from contrast agents, radiation exposure, and waste of time and money) + (harm from any invasive procedures that may follow the FP decision, such as liver biopsy) + (harm from unnecessary treatments) + (emotional distress) - (a slim theoretical benefit, such as an incidental detection of unrelated significant diseases on the follow-up tests) B: Absolute amount of net outcome gain in a single TP patient = (earlier diagnosis of the tumor, which may improve patient survival and allow for less invasive treatments with less treatment-related harm compared with later-stage diagnoses) - (small potential harm, such as adverse effects from treatments) |
Citation: Park SH, Sul AR, Han K, Sung YS. How to determine if one diagnostic method, such as an artificial intelligence model, is superior to another: beyond performance metrics. Korean J Radiol 2023;24(7):601-605